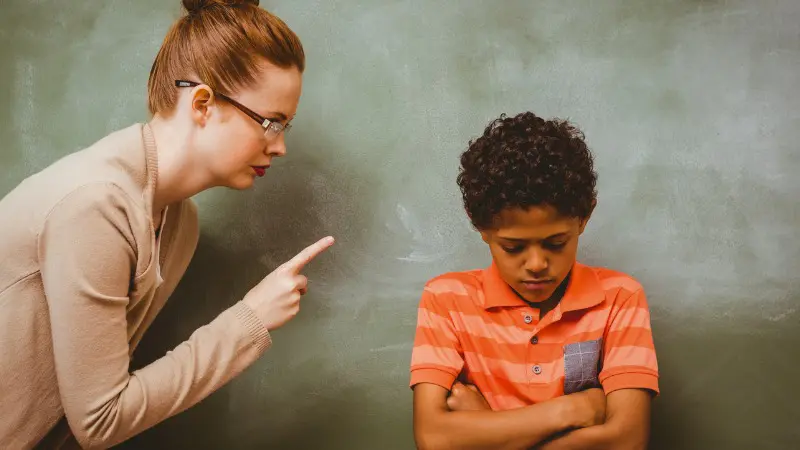
Creating an orderly and safe learning environment is essential for student success; however, disruptive behavior or academic dishonesty can sometimes disrupt that environment. At this point, to restore and maintain the order in the school, school punishments need to be introduced.
Effective school punishments are aimed to discourage negative and unwanted behaviors, encourage positive behaviors, and help students learn from their errors. These school punishments ranges from informal consequences to more serious interventions.
This article will explain in details, the different kinds of school punishments, allowing you to choose which best suits your school situation.
Table of contents
What is Punishment in School System?
Punishment in the school system refers to the application of consequences or disciplinary actions in response to student behavior that is deemed inappropriate, disruptive, or in violation of established rules and codes of conduct.
The primary goal of punishment in schools is to promote a safe, respectful, and conducive learning environment by addressing behavioral issues and encouraging responsible behavior.
It aims to teach students about the consequences of their actions, promote accountability, and maintain order within the educational setting.
Read Also: What is the Advantage of Applying learning Approaches To the Study of Personality
21 Types of School Punishments to Use in Schools in 2024
As classroom management techniques continue to evolve, it’s important to consider new approaches to maintaining discipline.
#1. Verbal Reprimands
One of the simplest yet effective forms of correction is the verbal reprimand. Educators can guide students toward better choices by addressing the behavior immediately and communicating the expectations.
#2. Time-Outs
Time-outs allow students to step back, reflect on their actions, and regain their composure. This technique encourages self-regulation and allows students to return to the classroom with a calmer mindset.
#3. Loss of Privileges
When students understand the correlation between their actions and the loss of privileges, they learn the importance of responsibility and accountability. This method encourages them to make thoughtful decisions.
#4. Extra Assignments
Assigning additional academic tasks can serve as a productive punishment. It reinforces learning and emphasizes the significance of responsibility and time management.
#5. Detention
Detention, when used constructively, offers students a structured environment to reflect on their behavior and consider choices. It allows them to recognize the consequences of their actions.
#6. Restorative Justice Circles
Restorative justice circles create a safe space for students to discuss their actions, understand the impact on others, and work towards resolution collaboratively. This approach strengthens the sense of community within the classroom.
#7. Behavior Contracts
Behavior contracts involve students setting goals and outlining the steps needed to improve their behavior. This collaborative approach empowers students to take ownership of their actions.
#8. In-Class Community Service
Engaging students in meaningful community service within the school environment helps them develop empathy, and a sense of civic responsibility.
#9. Peer Mediation
Peer mediation empowers students to resolve conflicts amicably with the guidance of trained peers. This technique equips students with lifelong conflict-resolution skills.
#10. Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs pair students with positive role models, fostering a supportive relationship that motivates good behaviour and personal growth.
#11. Counselling Sessions
Some behavioural problems stem from underlying emotional or psychological issues. Counselling sessions offer students a safe space to address these concerns and seek guidance.
#12. Mindfulness Practices
Introducing mindfulness practices helps students develop emotional regulation skills, enabling them to manage their impulses and reactions more effectively.
#13. Physical Activity
Incorporating physical activities as a discipline helps students channel their energy positively and constructively.
#14. Loss of Extracurricular Activities
Linking behaviour with participation in extracurricular activities encourages students to maintain a balance between their academic responsibilities and conduct.
#15. Parent-Teacher Involvement
Involving parents and guardians in addressing behavioural issues creates a unified approach. These school punishments reinforce consistent expectations between school and home.
Read Also: Do Colleges Look At Middle School Grades in 2024?
#16. Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement acknowledges and celebrates students’ good behaviour, motivating them to continue making positive choices.
#17. Structured Recess
Implementing structured recess activities allows students to develop social skills and learn to interact positively with their peers.
#18. Reflection Essays
Reflection essays prompt students to ponder their actions and the consequences, fostering deeper self-awareness and critical thinking.
#19. Apology Letters
Apology letters require students to take responsibility for their actions and empathize with those affected.
#20. Peer Reflection Panels
Peer reflection panels provide a platform for students to share and learn from each other’s experiences, creating a supportive and empathetic environment.
#21. Technology Time-Out
With the prevalence of technology, a temporary ban on gadgets during class can encourage active participation and reduce distractions, enabling students to engage more effectively.
See Also: Can I Get Student Loans Before School Starts? Best Expert Advice
Creative Punishments for Students in Schools
Creative punishments for students in schools aim to encourage learning, personal growth, and responsible behaviour while avoiding physical or harsh disciplinary methods.
These approaches focus on addressing misbehaviour constructively and engagingly.
Below are some creative punishment ideas that schools can consider:
- Service Learning Projects
- Reflection Journals
- Peer Tutoring
- Creative Writing Assignments
- Role-Play Scenarios
- Artistic Expressions
- Letter of Apology
- Creative Presentations
- Interactive Workshops:
- Mindfulness and Meditation
What Type of Punishment is Detention?
Detention is a disciplinary measure commonly used in schools to punish students who have engaged in minor misbehaviour or violated school rules.
It involves requiring the student to stay at school for a specified period outside of regular school hours, such as during lunch breaks, after school, or on weekends.
During detention, students are typically required to complete tasks or activities, reflect on their behaviour, or engage in other productive or corrective actions.
Detention is a milder punishment than more severe measures like suspension or expulsion.
What is Corporal Punishment in Schools?
Corporal punishment in schools is using physical force or pain to discipline students for perceived misbehaviour or rule violations.
This form of punishment involves actions such as spanking, paddling, caning, or any other physical act intended to cause discomfort or pain to the student.
Although corporal punishment often aims to deter undesirable behaviour and enforce compliance with school rules, using physical force may lead to fear, humiliation, and resentment among students.
This may affect their attitude toward school and learning. Hence, many countries and educational institutions have recognized its potential negative consequences.
Moreover, there is a growing understanding that effective discipline should focus on positive reinforcement, communication, and teaching appropriate behaviour.
While corporal punishment has been frowned upon recently, below is a list of school punishments still in schools.
Examples of Corporal Punishments
Here are some examples of corporal punishments that were practiced in various settings:
- Spanking or Slapping
- Paddling
- Forced Postures
- Caning
- Whipping.
- Flogging
- Birching
- Strapping
- Switching
- Slugging
- Ear Pulling
- Hair Pulling
- Kneeling on Grains
- Forced Exercise
- Pinching or Twisting
When Was Corporal Punishment Banned in Schools?
The timeline for banning corporal punishment in schools varies from country to country and even within different regions.
For instance, Sweden banned corporal punishment in schools in 1958, while Germany’s ban came into full force in 2000.
The use of corporal punishment in schools is regulated at the state level. Many states have banned it in the United States, while others still allow it to varying degrees. Over 31 states in the US have a law that bans this act in schools.
In the UK, it was banned in England and Wales in 1987, Scotland in 1982, and Northern Ireland in 2003.
Why is Missouri bringing back corporal punishment?
On 27th August last year, Superintendent Merlyn Johnson explained that Missouri corporal punishment occurs after a survey.
This survey revealed parents, students, and school employees were concerned about student behaviour and discipline. He reiterated that people have commended them for this step towards instilling discipline.
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled in 1977 that corporal punishment is constitutional and left it up to states to set their policies. Craven said 19 states, many in the South, have laws allowing it in schools.
FAQs
Parents can support these punishments by reinforcing lessons at home and collaborating with educators to maintain consistent expectations.
Positive punishments are the most effective kind of punishment.
Punishments that encourage self-awareness and discussion rather than humiliation or embarrassment.
These punishments can be adapted to different age groups with appropriate modifications.
Restorative justice circles promote open communication, empathy, and conflict-resolution skills among students.
Conclusion
School punishments are not a one-size-fits-all solution to every school problem. While some problems require stricter, more serious measures to address, other challenges only require an informal punishment option.
The most effective punishments are those that are fair, consistent and focused on helping students learn and grow. In all, the various kinds of school punishments allow you to tailor an appropriate response to the severity of the offence and the individual student’s needs.
References
- Youth Rights.org – POLICING AND PUNISHMENT IN SCHOOLS
- Wikipedia.com – School punishments
- Think Student.co.uk – 15 Types of Punishment Used in Schools in 2024