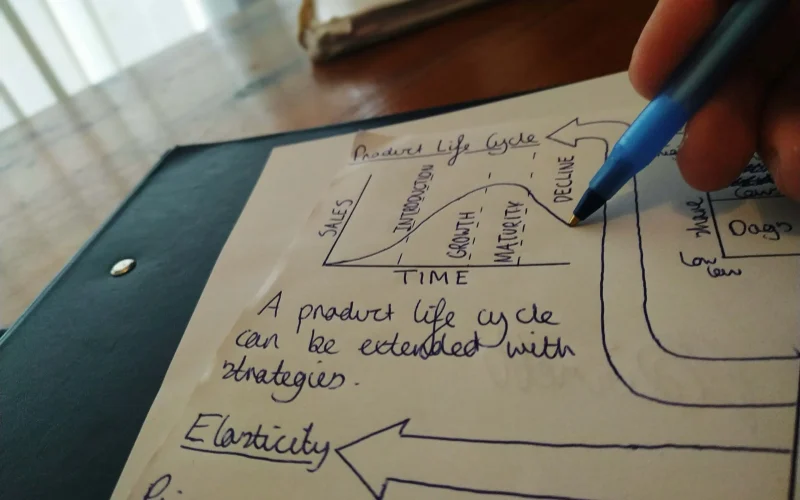
Most times, studying can be a difficult task, especially when you are faced with a mountain of information to retain. It is possible that reading textbooks aloud and highlighting key points isn’t the most efficient way to learn and remember information. Mind Maps come into play in this situation.
The Mind map is a powerful tool waiting to be discovered in your learning arsenal. These dynamic diagrams are more than just colorful scribbles; they’re a game-changer for effective revision and knowledge retention.
Mind Maps are an invaluable resource for effective revision because they are visual tool that can help you organize and remember information more effectively. In this article, we will explore how to use mind maps effectively for revision while studying.
Table of contents
What is a Mind Map?
A mind map is a graphical representation of information, ideas, or concepts. Most of the time, it starts with a big idea or topic that is represented by a big picture or word. From there, branches that spread outward connect connected concepts and sub-topics.
Mind maps use tones, images, and watchwords to make associations and relationships between various snippets of data, making them an amazing asset for memory maintenance and perception.
Why Use a Mind Map?
Using a mind map offers several advantages and benefits, making it a valuable tool in various aspects of life, including education, problem-solving, creativity, and organization. Here are some compelling reasons to use a mind map:
- Enhanced Memory Retention
- Effective Learning Aid
- Improved Comprehension
- Efficient Organization
- Creative Problem Solving
- Time-Saving
- Versatility
- Stress Reduction
- Effective Communication
- Customization
- Goal Setting and Planning
- Stimulates Creativity
- Easier Review
Also Read: What is the Difference Between Foundation and Higher Tier at GCSE?
What are the Benefits of Using Mind Maps for Revision?
There are various benefits associated with using a mind map for revision. Here are some.
- Visual Organization: Mind maps provide a visual representation of information, which can make complex topics more digestible. This visual structure helps you see the big picture and the relationships between different concepts.
- Active Engagement: Creating a mind map requires active engagement with the material. This process of synthesis helps you understand and remember the information more effectively than passive reading.
- Memory Retention: The combination of text, colors, and images in a mind map helps your brain encode and retain information more efficiently. The visual cues make it easier to recall details during exams.
- Efficient Review: Mind maps condense information into a concise format, making it easier to review the entire topic quickly. This is especially useful when you’re short on time.
Drawbacks of Using a Mind Map for Revision
While mind maps are generally a powerful and effective tool for revision and learning, they may not be suitable for every individual or situation. Here are some potential drawbacks of using mind maps for revision:
- Time-Consuming Creation: Creating a detailed and well-structured mind map can be time-consuming, especially if you’re dealing with a large volume of information.
- Complex Subjects: For highly complex or technical subjects, creating a comprehensive mind map can be challenging.
- Learning Style Compatibility: Mind maps may not align with everyone’s preferred learning style.
- Initial Learning Curve: If you’re not familiar with creating mind maps or using mind mapping software, there may be an initial learning curve.
- Overuse: While mind maps are a valuable tool, relying solely on them for all types of revision can lead to a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Digital Distractions: When using digital mind mapping tools, distractions such as notifications, internet access, or multitasking can hinder the revision process.
- Dependency on Visual Aids: Overreliance on mind maps can make students dependent on visual aids for comprehension, potentially hindering their ability to absorb information through other methods.
- Portability: Physical mind maps created on paper may not be as portable or easily accessible as digital versions.
Types of Mind Maps
Mind maps are versatile tools that can be adapted to various purposes and situations. Here are some common types of mind maps:
- Simple Mind Map: The typical mind map has a central topic or idea at its center, and main branches that represent subtopics or categories extend outward from there. Information can be further broken down into more specific details using sub-branches.
- Idea Guide: Like an essential psyche map, an idea map centers around representing connections between various ideas or thoughts. It frequently incorporates connecting expressions or lines between hubs to explain associations.
- Flowchart Brain Guide: This kind of psyche map stresses the progression of cycles, steps, or successions. It is valuable for imagining work processes, choice trees, and venture courses of events.
- Mind Map for the Organization: Hierarchical brain maps assist with organizing considerations connected with undertakings, tasks, or occasions. They frequently incorporate segments for objectives, errands, cutoff times, and obligations.
- Mind Map Matrix: A matrix mind map combines elements of a matrix (grid) with a traditional mind map. It’s useful for comparing and contrasting multiple concepts, objects, or criteria.
- Timeline Mind Map: Timeline mind maps visually represent chronological events or historical timelines. They help you understand the sequence of events and their relationships.
- Decision-Making Mind Map: This type of mind map aids in making decisions by mapping out various options, their pros and cons, and potential outcomes. It helps you visualize the decision-making process.
- Study Aid Mind Map: Study aid mind maps are used to summarize and revise information for educational purposes. They condense complex subjects into a visually appealing format to aid learning.
- Problem-Solving Mind Map: Problem-solving mind maps help you analyze and solve complex problems by breaking them down into components, identifying possible solutions, and evaluating their feasibility.
How do I Use Mind Maps Effectively for Revision While Studying?
Using mind maps effectively for revision while studying can greatly enhance your understanding, retention, and recall of information. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to make the most of mind maps during your revision process:
Choose your Primary Subject
Begin by distinguishing the primary subject or idea you need to study. In the middle of your paper or digital canvas, write it. It will serve as the core of your mind map.
Create Main Branches
From the central topic, make main branches that each represent an important subtopic or category related to your main topic. Use a single word or a short expression to mark each branch.
Include Sub-branches
For every principal branch, add sub-branches to separate the data. These sub-branches should be labeled with keywords or brief phrases.
Use Visual Elements
Incorporate visual elements such as colors, icons, and images to make your mind map visually appealing and memorable. Different colors can represent different categories or themes, while icons and images can provide visual cues to enhance understanding.
Keep It Basic
Don’t fill your mind map with too many details. Focus on capturing the most essential information. Use keywords, short phrases, or abbreviations to keep the content concise and easily digestible.
Maintain Consistency
Keep a consistent structure in your mind map. Use the same shapes, colors, and formatting throughout to make the map easy to follow. Consistency aids in creating a clear and organized visual representation of your knowledge.
Connect Ideas
Show the flow of information by connecting related concepts with lines or arrows. This helps you see how various ideas are connected.
Prioritize Key Points
Highlight or emphasize key points within your mind map. These could be critical facts, formulas, dates, or any information that you need to remember distinctly. Visual cues like bold text or larger fonts can be effective for this purpose.
Audit and Modify
Intermittently audit and update your psyche map as you study. This will assist with building up your comprehension and guarantee you miss no basic focuses.
Practice Retrieval
After creating your mind map, use it actively for studying. Cover parts of the mind map and try to recall the associated information. This practice enhances memory retention and ensures you truly understand the material.
Create Multiple Mind Maps
If your subject matter is extensive, consider creating multiple mind maps, each focusing on a specific sub-topic or chapter. This helps in keeping your revision organized and manageable.
Use Digital Tools
Consider using digital mind mapping tools and apps like MindMeister, XMind, or even simple tools like Microsoft OneNote or Google Drawings. Digital formats can be easier to edit and share.
If you’re studying with others, you can collaborate by sharing your mind maps. This can be an effective way to exchange knowledge and gain new insights.
Read: Is There a Maximum Age for University in the UK?
FAQs on Mind Map Revision
Mind maps are adaptable and useful for a wide range of subjects. They are especially valuable when you really want to sum up complex data, make associations between thoughts, or make an organized outline of a subject.
Yes, many digital tools and software applications are available for creating mind maps.
Focus on key concepts, main ideas, and important details. Avoid overwhelming your mind map with excessive information.
It’s not always necessary to create a new mind map from scratch. You can revise and update existing mind maps as you gain deeper insights or progress in your studies.
Conclusion
While you revising for your exams, Mind Maps can be a very useful constant companion. They will not only solidify your understanding of key concepts but also serve as good tool for test preparation.
With that, you can identify knowledge gaps and tailor your study sessions for maximum productivity. The flexibility, adaptability, and ability of Mind Map to stimulate creative thinking, make them a popular and effective method for improving memory.